Indigenous non-profit looks to acquire ownership of Trans Mountain Pipeline
 Pipe for the Trans Mountain pipeline is unloaded in Edson, Alta. on Tuesday, June 18, 2019. (THE CANADIAN PRESS/Jason Franson)
Pipe for the Trans Mountain pipeline is unloaded in Edson, Alta. on Tuesday, June 18, 2019. (THE CANADIAN PRESS/Jason Franson)
A new Indigenous non-profit organization is seeking an ownership stake in the Trans Mountain Pipeline, saying its aim is to make sure communities along the pipeline's route receive its benefits directly.
Nesika Services publicly launched Monday, calling itself a grassroots, community-led not-for-profit.
Chief Tony Alexis of the Alexis Nakota Sioux Nation in Alberta (and the chair and founding director of Nesika) said 14 Indigenous communities along the pipeline's route in Alberta and B.C. have already signed on.
He said Nesika is in the process of reaching out to all 129 communities that have been identified by the federal government as being impacted by Trans Mountain to ensure they have a chance to join in.
"Ultimately what we're trying to do right now is to organize the communities,'' Alexis said in an interview. "Once Canada has decided they're willing to sell this pipeline, then at that time we'll be negotiating to purchase."
The Trans Mountain pipeline carries 300,000 barrels of oil per day, and is Canada's only pipeline system transporting oil from Alberta to the West Coast.
It was bought by the federal government for $4.5 billion in 2018, after previous owner Kinder Morgan Canada Inc. threatened to scrap the pipeline's planned expansion project in the face of environmentalist opposition.
Under the ownership of Trans Mountain Corp., a federal Crown corporation, the Trans Mountain expansion project is currently underway, and Prime Minister Justin Trudeau has indicated that he is open to ownership of the pipeline by Indigenous groups.
Several Indigenous-led initiatives have already come forward. Project Reconciliation is seeking a 100 per cent ownership stake in the pipeline with no equity requirement or liability risk to Indigenous partners. Its goal is to distribute cash flow from the pipeline between the participating Indigenous community owners, and an Indigenous Sovereign Wealth Fund that will invest in energy transition projects.
Chinook Pathways – which is also seeking an equity stake – is an Indigenous-led partnership formed by Western Indigenous Pipeline Group and its industry partner, Pembina Pipeline Corp.
What sets Nesika Services apart from these other proposals, Alexis said, is that it is a true not-for-profit not backed by industry or affiliated with financial institutions or any other operating parties.
"These groups, these other groups, they are profit-oriented, which is a major conflict for Indigenous communities," Alexis said.
"For me, as a community leader, when I look at Nesika, it provides the best opportunity for us to build our wealth and grow our communities. Resources are needed within the communities and Nesika provides that kind of opportunity for us."
Alexis said Nesika is exploring both equity and revenue sharing opportunities in Trans Mountain with no up-front capital requirements from participating groups.
He declined to see how a potential purchase would be financed, saying that will be determined once the government of Canada makes the potential terms of a sale clear.
The federal government has not yet accepted any bids for the pipeline, though Alexis said he expects negotiations with interested parties to begin "within a month or two."
Nesika's other founding directors include Chief Alice McKay of Matsqui First Nation, Coun. David Walkem of Cook's Ferry Indian Band, and Mark Peters from Peters First Nation.
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Jan. 24, 2022.
CTVNews.ca Top Stories
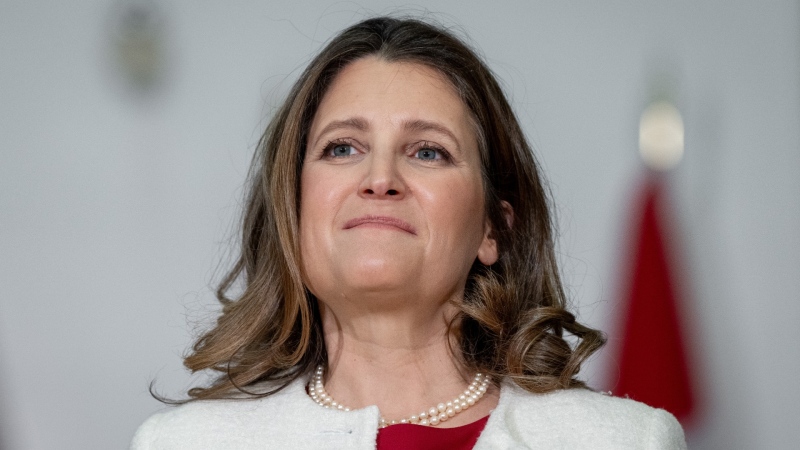

NEW Freeland to present 2024 federal budget, promising billions in new spending
Canadians will learn Tuesday the entirety of the federal Liberal government's new spending plans, and how they intend to pay for them, when Deputy Prime Minister and Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland tables the 2024 federal budget.
Ontario woman charged almost $7,000 for 20-minute taxi ride abroad
An Ontario woman was shocked to find she’d been charged nearly $7,000 after unknowingly using an unauthorized taxi company while on vacation in January.
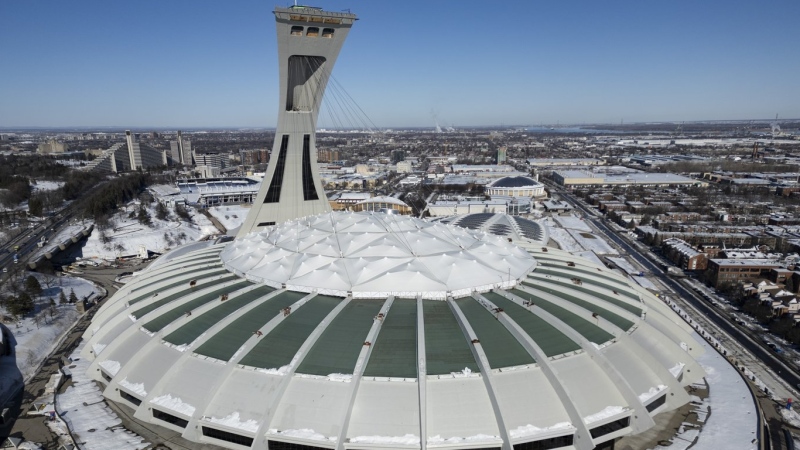
Worker seriously injured after fall at Montreal Olympic Stadium
A man is fighting for his life after falling about 30 feet in an air duct at Montreal's Olympic Stadium on Monday, authorities say.
Tim Hortons launches pizza nationally to 'stretch the brand' to afternoon, night
Tim Hortons is launching flatbread pizzas nationally in a bid to pick up more afternoon and evening customers.
A look inside the gutted 24 Sussex Drive
The National Capital Commission is providing a glimpse inside the gutted 24 Sussex Drive, more than a year after the heritage building along the Ottawa River was closed.
NASA confirms mystery object that crashed through roof of Florida home came from space station
NASA confirmed Monday that a mystery object that crashed through the roof of a Florida home last month was a chunk of space junk from equipment discarded at the International Space Station.
Hazard ahead: Are cuts at Tesla a warning sign for the EV market in Canada?
Tesla has hit a series of roadblocks, including increased competition and declining sales. The company announced Monday it is slashing 10 per cent of its global workforce.
Fire rages through the 17th-century Old Stock Exchange in Copenhagen, toppling the iconic spire
A fire raged through one of Copenhagen's oldest buildings on Tuesday, causing the collapse of the iconic spire from the 17th-century Old Stock Exchange as passersby rushed to help emergency services save priceless paintings and other valuables.
Budget 2024 'likely to be the worst' in decades, former BoC governor says
Without having seen it, former Bank of Canada governor David Dodge believes that Tuesday's 2024 federal budget from Deputy Prime Minister and Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland is 'likely to be the worst budget' in decades.