'Permanent bone loss': Calgary study finds astronauts suffer on return to Earth
 FILE - Canadian astronaut Robert Thirsk talks with students from Rockcliffe Elementary School as they get a first look at The Living In Space exhibit during its unveiling at the Canadian Aviation and Space Museum in Ottawa on Thursday, May 12, 2011. (THE CANADIAN PRESS/Sean Kilpatrick)
FILE - Canadian astronaut Robert Thirsk talks with students from Rockcliffe Elementary School as they get a first look at The Living In Space exhibit during its unveiling at the Canadian Aviation and Space Museum in Ottawa on Thursday, May 12, 2011. (THE CANADIAN PRESS/Sean Kilpatrick)
The experience may be out-of-this-world but research indicates those who travel to outer space suffer from increased bone loss.
A study released Thursday from the Cumming School of Medicine at the University of Calgary followed 17 astronauts before and after their space flights.
The TBone study, conducted over a seven-year period starting in 2015, found that prolonged weightlessness accelerated bone loss in the astronauts.
"We found that weight-bearing bones only partially recovered in most astronauts one year after spaceflight," said Dr. Leigh Gabel, an assistant professor in the faculty of kinesiology and lead author of the study.
"This suggests the permanent bone loss due to spaceflight is about the same as a decade worth of age-related bone loss on Earth."
The researchers travelled to Johnson Space Center in Houston to scan the wrists and ankles of the astronauts before they left for space, on their return to Earth then after six months and one year.
The findings, published in Scientific Reports, said the loss happens because bones that would normally be weight-bearing on Earth, such as the legs, don't have to carry weight in a zero gravity setting.
"We've seen astronauts who had trouble walking due to weakness and lack of balance after returning from spaceflight to others who cheerfully rode their bike on Johnson Space Center campus to meet us for a study visit," said Dr. Steven Boyd, director of the McCaig Institute for Bone and Joint Health and professor in the Cumming School of Medicine.
"There is quite a variety of response among astronauts when they return to Earth."
The study found some astronauts who flew on shorter missions, under six months, recovered bone strength and density in the lower body compared to those who flew for longer durations.
As future space missions are exploring travel to more distant locations, the study's next iteration plans to look at the effects of even longer trips, to support astronauts who may one day travel beyond the International Space Station.
The University of Calgary's former chancellor and astronaut, Robert Thirsk, said he knows how difficult it can be to be back on solid ground.
"Just as the body must adapt to spaceflight at the start of a mission, it must also readapt back to Earth's gravity field at the end," he said.
"Fatigue, light-headedness and imbalance were immediate challenges for me on my return. Bones and muscles take the longest to recover following spaceflight. But within a day of landing, I felt comfortable again as an Earthling."
The study was funded by the Canadian Space Agency in partnership with the European Space Agency, NASA and astronauts from North America, Europe, and Asia.
This report by The Canadian Press was first published June 30, 2022.
CTVNews.ca Top Stories
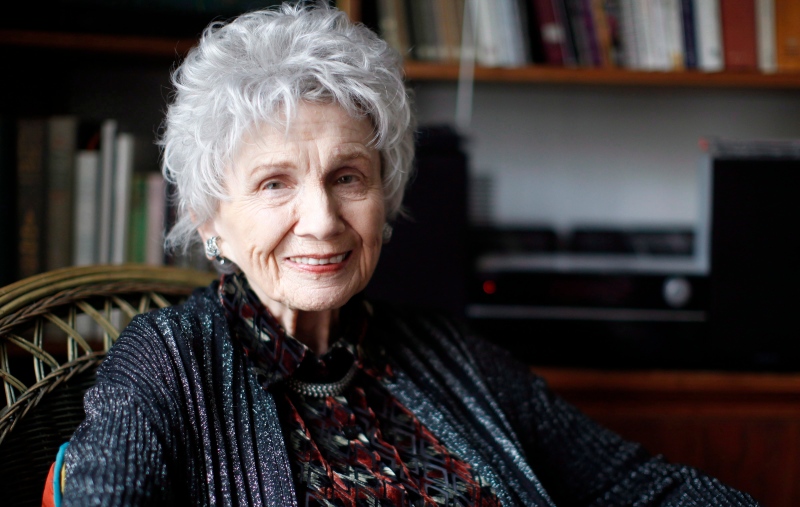

BREAKING Alice Munro, Nobel literature winner revered as short story master, dead at 92
Nobel laureate Alice Munro, the Canadian literary giant who became one of the world's most esteemed contemporary authors and one of history's most honoured short story writers, has died at age 92.
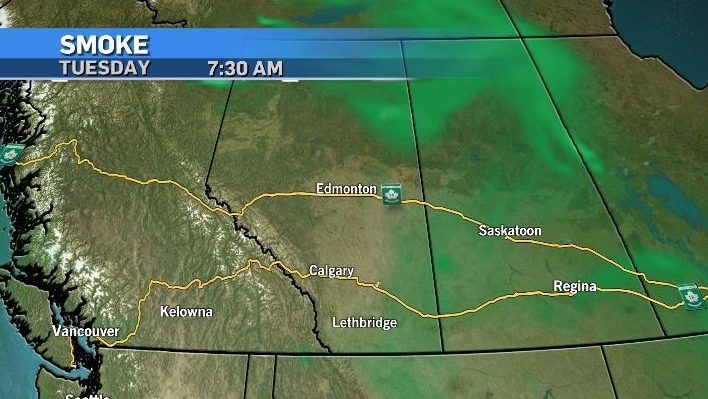
Latest updates on air quality alerts, and when the smoke may reach Ontario and Quebec
Wildfires have led Environment Canada to issue air quality advisories for parts of B.C., Alberta, Manitoba, Saskatchewan and the Northwest Territories, as forecasters warn the smoke could drift farther east.
Are these Canada's best restaurants? Annual top 100 list revealed
The annual list of Canada's top restaurants in the country was just released and here are the places that made the 2024 cut.
Attack on prison van in France kills 2 officers, inmate escapes
Armed assailants killed two French prison officers and seriously wounded three others in an attack on a convoy in Normandy on Tuesday and an inmate escaped, officials said.
Steal a car, lose your driver's licence for 10 years under new Ontario proposal
Repeat car thieves may face lengthy licence bans under proposed changes to Ontario’s Highway Traffic Act.
$1.6B parts plant for Honda electric vehicle batteries coming to Niagara Region
A Japanese company has announced it will build an approximately $1.6-billion plant in Ontario's Niagara Region that will make a key electric vehicle battery component as part of Honda's supply chain in the province.
B.C. brings in law on name changes on day that child killer's new identity revealed
The BC NDP have tabled legislation aimed at stopping people who have committed certain heinous acts from changing their names.
Manitoba premier to visit areas impacted by wildfire
Manitoba Premier Wab Kinew will get a close-up look at the devastation from a large wildfire burning in northern Manitoba Tuesday.
Significant police presence as Israeli flag flies at Ottawa City Hall
The Israeli flag is flying at Ottawa City Hall today to mark the country's national day, with plans to hold a private ceremony to mark Israel's Independence Day. There is a significant police presence at City Hall, including security barriers outside the main doors.